
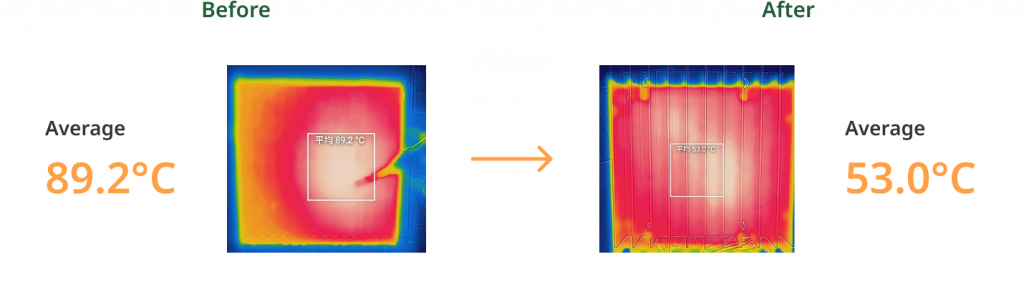
The IPC thermal solution normally determined by its mechanical design, surface treating and airflow condition. For thermal design of a high-end IPC, the requirements for working in high-temperature environment or high-performance purpose, the fin area is needed for achieving the design goal of low thermal resistance and usually tuned via controlling the height. If compact design is required, another way is redefinition of airflow in an environment or the use of fan.



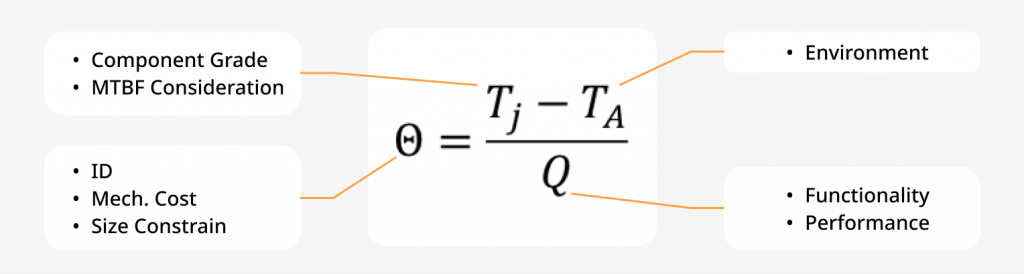
Once the heat sink, pads, PCB, and chassis that make up the thermal path from the inside to the outside can be approximated as a resistor network, the thermal problem can be analyzed, tuned, and resolved according to the above formula.
Copyright© MiTwell, Inc. All rights reserved.